There’s something about gold. It possesses us, sometimes entire nations to accumulate more and more of it. Humans have had a strong affinity for gold since the times of the ancient Egyptians and the Aztecs. Gold has been used as currency for thousands of years. Wars have been fought for it, entire civilizations slaughtered for their gold. Pindar, the ancient Greek poet, described gold as “a child of Zeus, neither moth or rust devoureth it, but the mind of man is devoured by this supreme possession.”
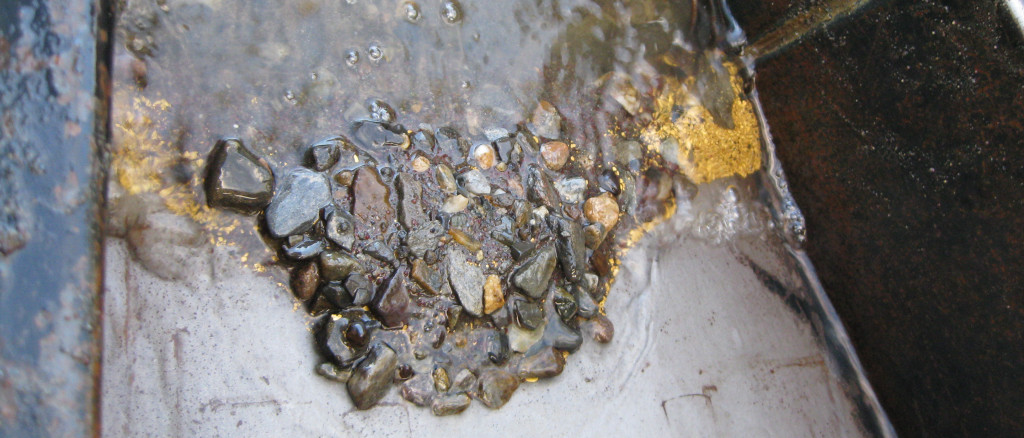
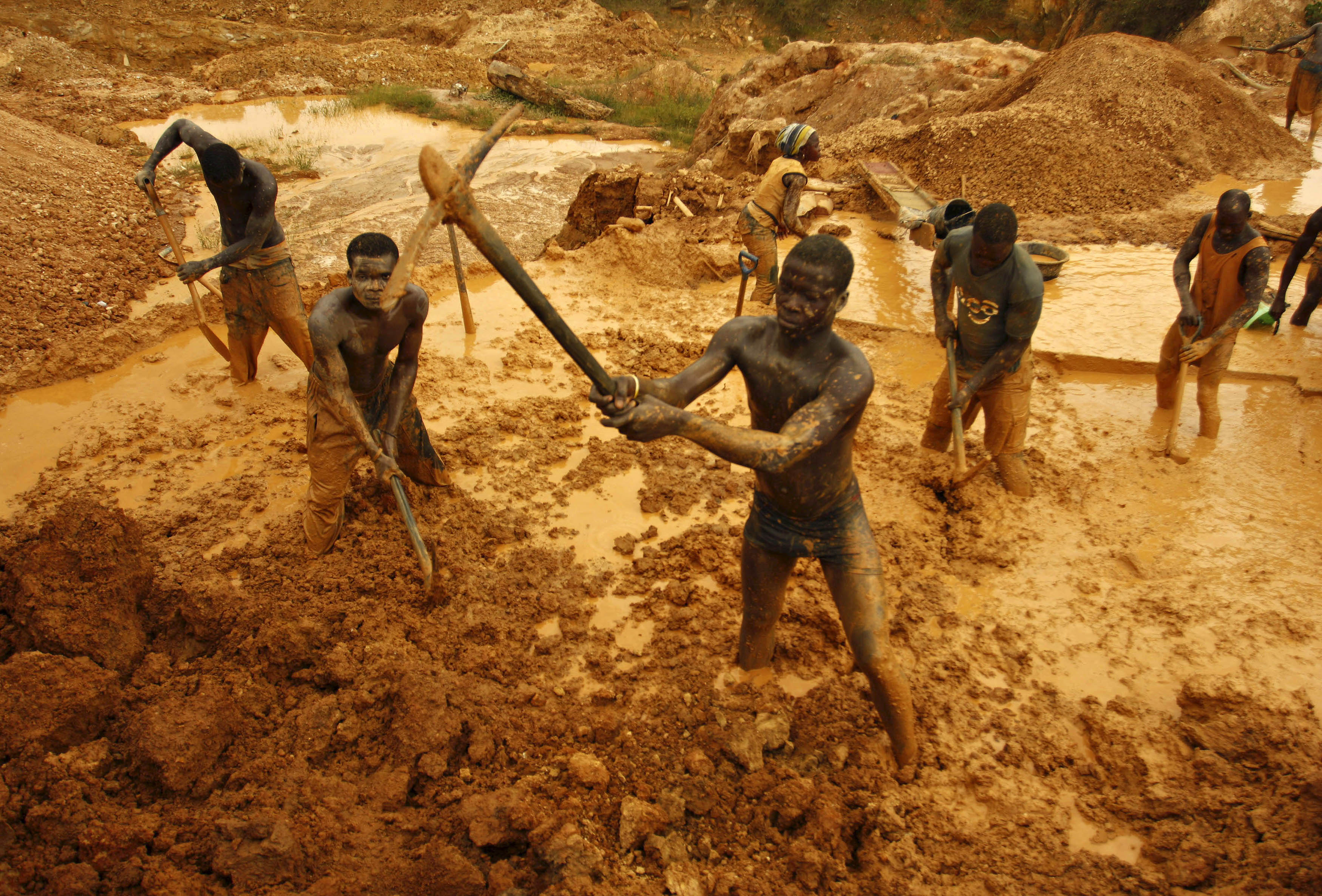
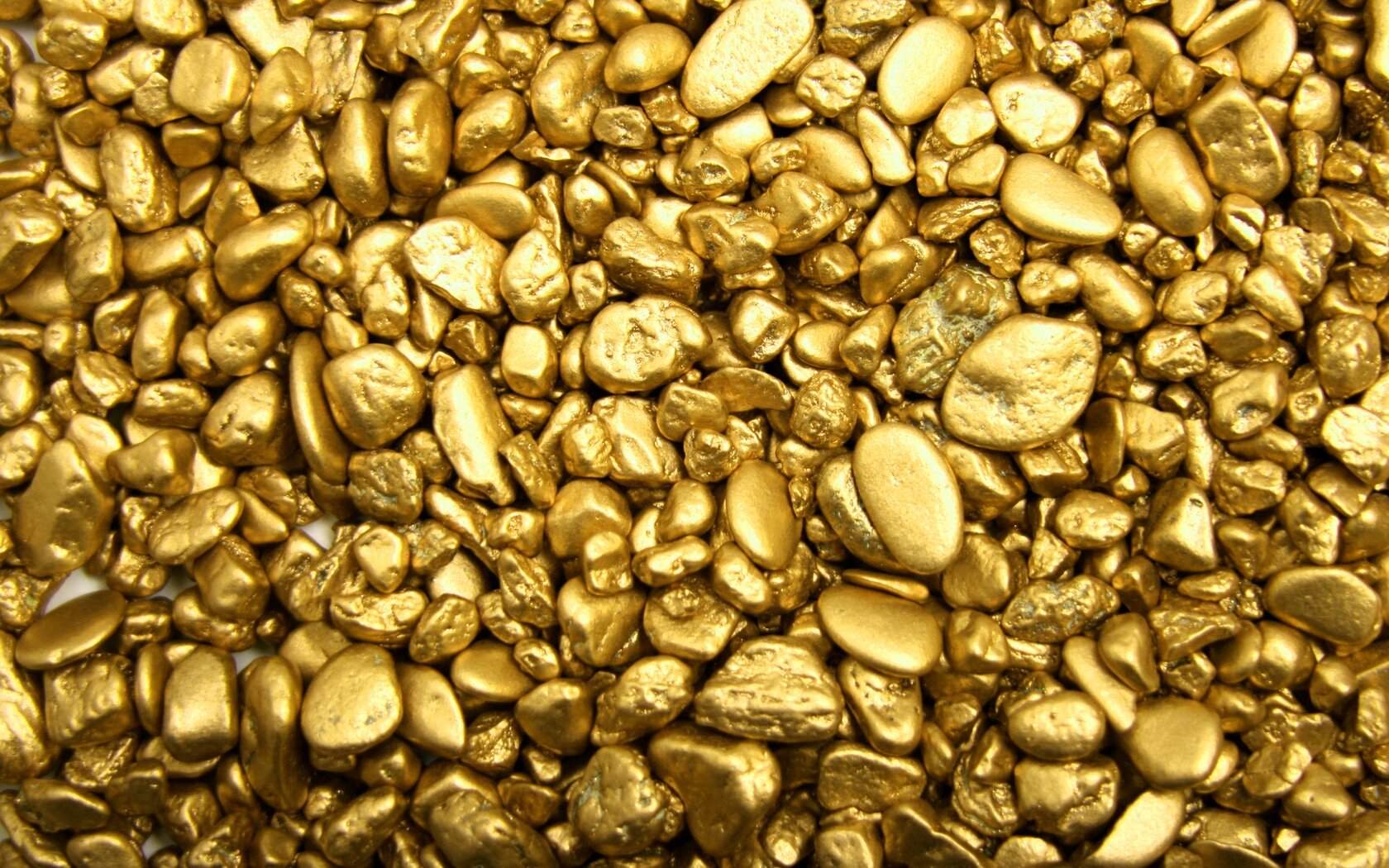
It’s hard to describe the feeling of finding your first gold nugget in an old stream bed. It sits there in your pan shimmering, the way that only gold can. You immediately recognize it’s power, it is intoxicating. This is what drives prospectors past and present to take great risks in the search for gold. There’s more than just the value of gold that attracts us to it. The word “placer” itself comes from the Spanish word meaning “pleasure”. For some it is an addiction, for others it symbolizes wealth. You’ll be hard pressed to find a member of the human species who wouldn’t be interested in some gold.
Gold has several properties that make it desirable. Most importantly it does not rust or tarnish. Gold artwork discovered in the tombs of Egypt looks just as lustrous today as it did 5000 years ago. Why is that? Gold belongs to a group of metals called the “Noble Metals”. They’re called noble because like nobility in old time monarchies they don’t associate with others. It’s fancy way of saying that the metals don’t readily react. Conversely iron will readily react with oxygen to form iron oxide (aka rust). Gold and other noble metals, such as platinum, possess a very strong atomic structure that requires a lot of energy to disrupt.
The ability to maintain over time is common of all valuable substances. A diamond for example produces a characteristic glow when cut and faceted properly but what good would it be if it disintegrated a month later? Diamonds are extremely hard and have a rock solid crystal structure. Other valuable gemstones all share similar properties, emeralds, rubies, sapphires and garnets all sit at the high end of the hardness scale. While gold isn’t hard in a geological sense it maintains it’s shape and luster indefinitely.
Gold is also very malleable. Meaning that it can be hammered or pressed into various shapes without cracking or losing its consistency. You could stretch an ounce of gold into a wire 80km long or produce a sheet of gold leaf 80 meters by 80 meters wide. Gold is also an excellent conductor. Not quite as good as copper but a better conductor than nickel, brass, iron, tin, and aluminium. Gold conductive wire is used in many critical electronics applications such as computer motherboards, smart phones and satellites.
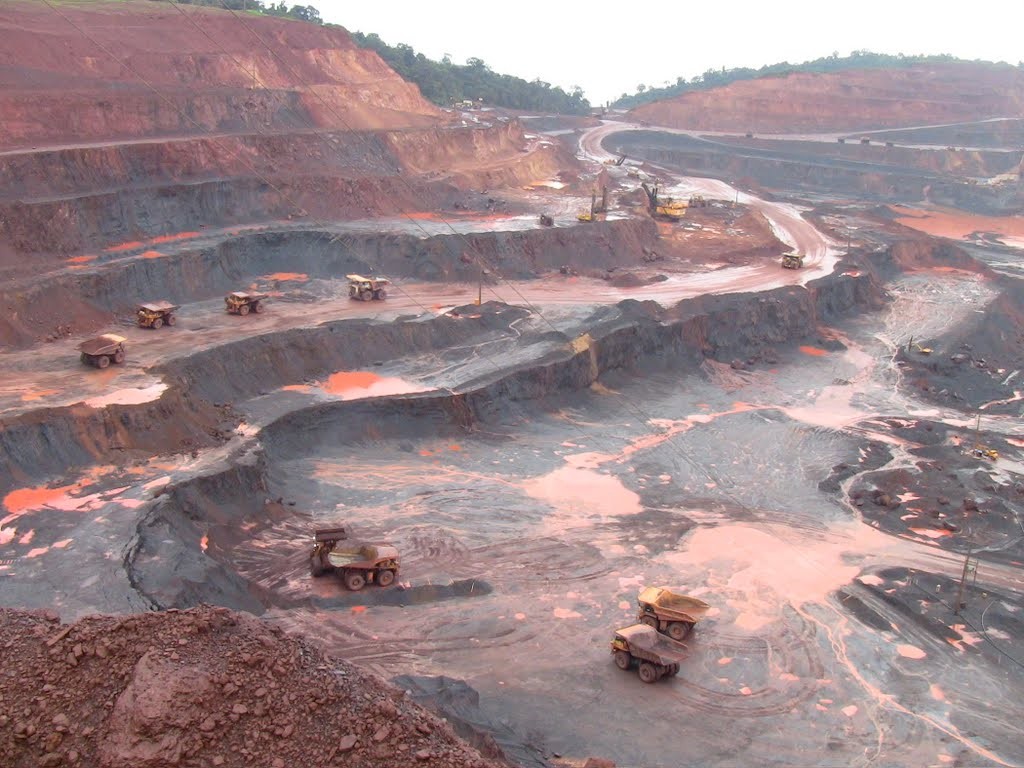

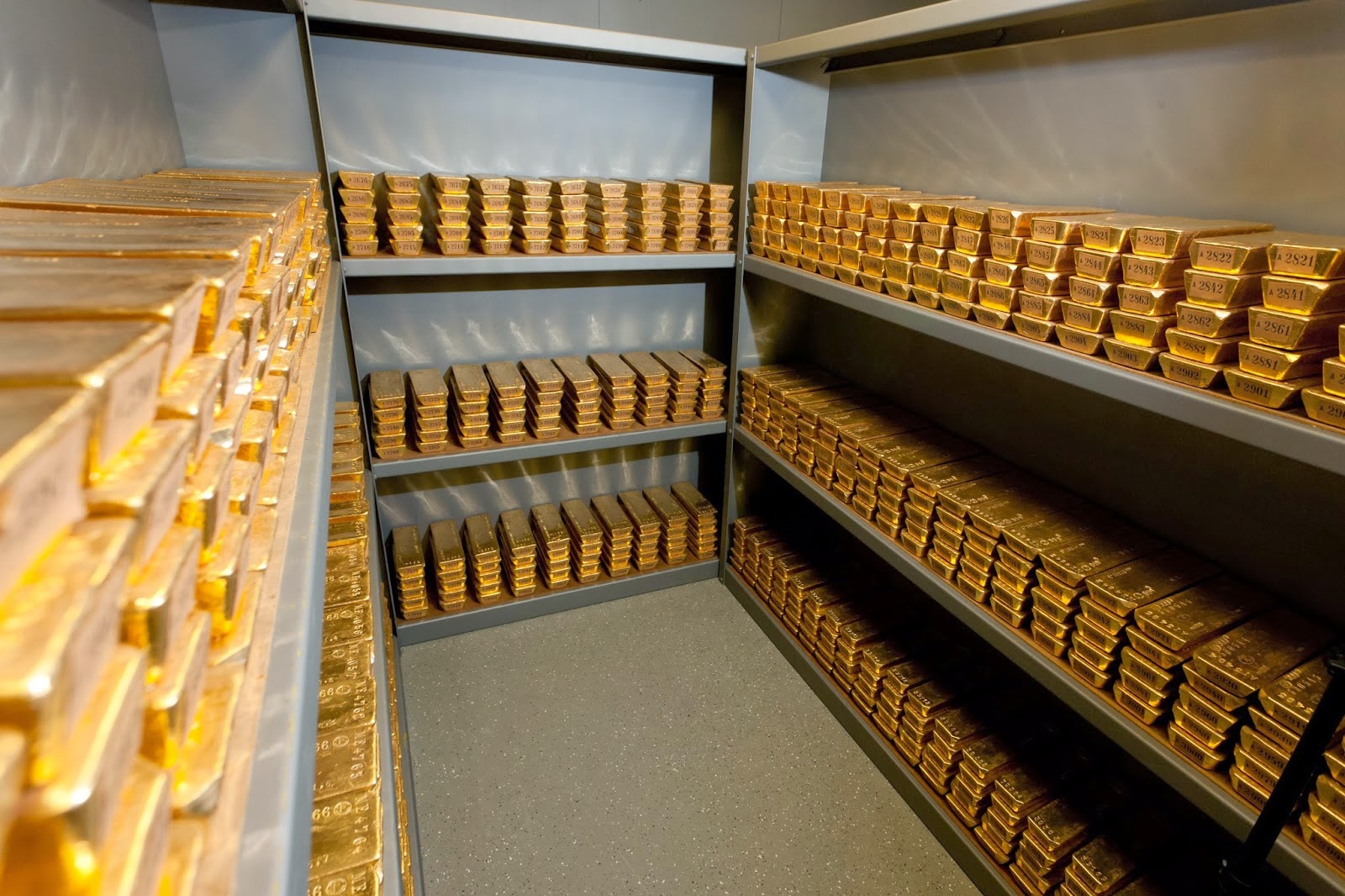
What really makes gold valuable though is it’s scarcity at the earth’s surface. Approximately 165,000 metric tons of gold have been produced in the entirety of human history. While that may sound like a lot the amount of gold produced by mining is extremely small in comparison to other metals. For example the Carajás Mine in Brazil produces an average of 300 million metric tons of iron per year and has a deposit estimated at 7.2 billion metric tons. And that’s just one mine. All the gold ever produced would fit inside one Olympic sized swimming pool.
It is often stated that you can’t eat gold. While that’s not entirely true, (see gold covered pizza) an all gold diet wouldn’t provide much nutrition, and you’d probably have some digestive issues. The yellow metal doesn’t appeal to our basic needs for survival but neither does money or a smartphone. That doesn’t make any of these things less valuable.
We typically think of value in dollar terms. When evaluating an investment such as stocks or real estate it’s hard to think of anything else. Dollars are not constant though, they are subject to manipulation and inflation. For at least 6000 years gold has been used as currency and unlike modern currency is not subject to inflation. Modern currencies are what is called “Fiat Currency”. There is no standard on what a modern currency note can be exchanged for. Their value relies solely on people’s faith in it. Or more correctly their faith in the government. Inflation rates can severely affect the spending power of a dollar. There are countless examples, the most striking is the inflation of the German Reichsmark which rose from 4.2 marks to USD in 1914 to a peak of around 4.2 trillion marks to the US dollar by November 1923. At that time a wheelbarrow full of German marks wouldn’t even buy a newspaper.
Historically world currencies were backed by the gold standard which meant that by law any amount of paper money could be exchanged for a specified amount of gold. In the 1920s each US dollar was backed by 1.5 grams of gold. The dropping of the gold standard in Germany during WWI allowed for the hyperinflation that followed. The United States dropped the standard during the great depression to avoid the federal gold supply from being completely depleted. Canada followed suit in 1933. There’s much debate on the merits of dropping the gold standard. What resulted though is the ability for the government to completely control the currency without requiring tangible assets (ie. gold) to back it up.

So if the dollar is backed by nothing and can be manipulated at will how do you gauge the value of gold. Or anything for that matter. True value depends on what people are willing to trade for your goods. Money makes it easy to barter and trade goods since it’s ubiquitous and there is an agreed upon value at any given time. For example if you want to sell your car on craigslist you’ll have an idea of how many dollars you want for it. Lets say you have a used Honda Civic. You could sell that easily for $4000 CAD. That same Honda Civic could be traded for a 1 carat diamond engagement ring. 50 years from now a used car might sell for $25,000 dollars due to inflation but the exchange rate of car to diamond ring would remain the same.
The old adage that an ounce of gold will buy you a nice suit still rings true today. In the gold rush era (1848-1900) an ounce of gold would trade for about $20 USD, and would also buy a nice suit. A typical suit today would cost you about $450 USD. So it would seem that today’s gold would buy you 3.5 nice suits. You have to consider that in the 1800s nice clothing was not mass produced. To compare accurately you’d have to look at a tailored suit. A mid range tailored suit made in the United States costs between $1650 and $1800 today. At present gold is trading at about $1250 USD so the suit adage falls just above the quoted dollar value of gold.
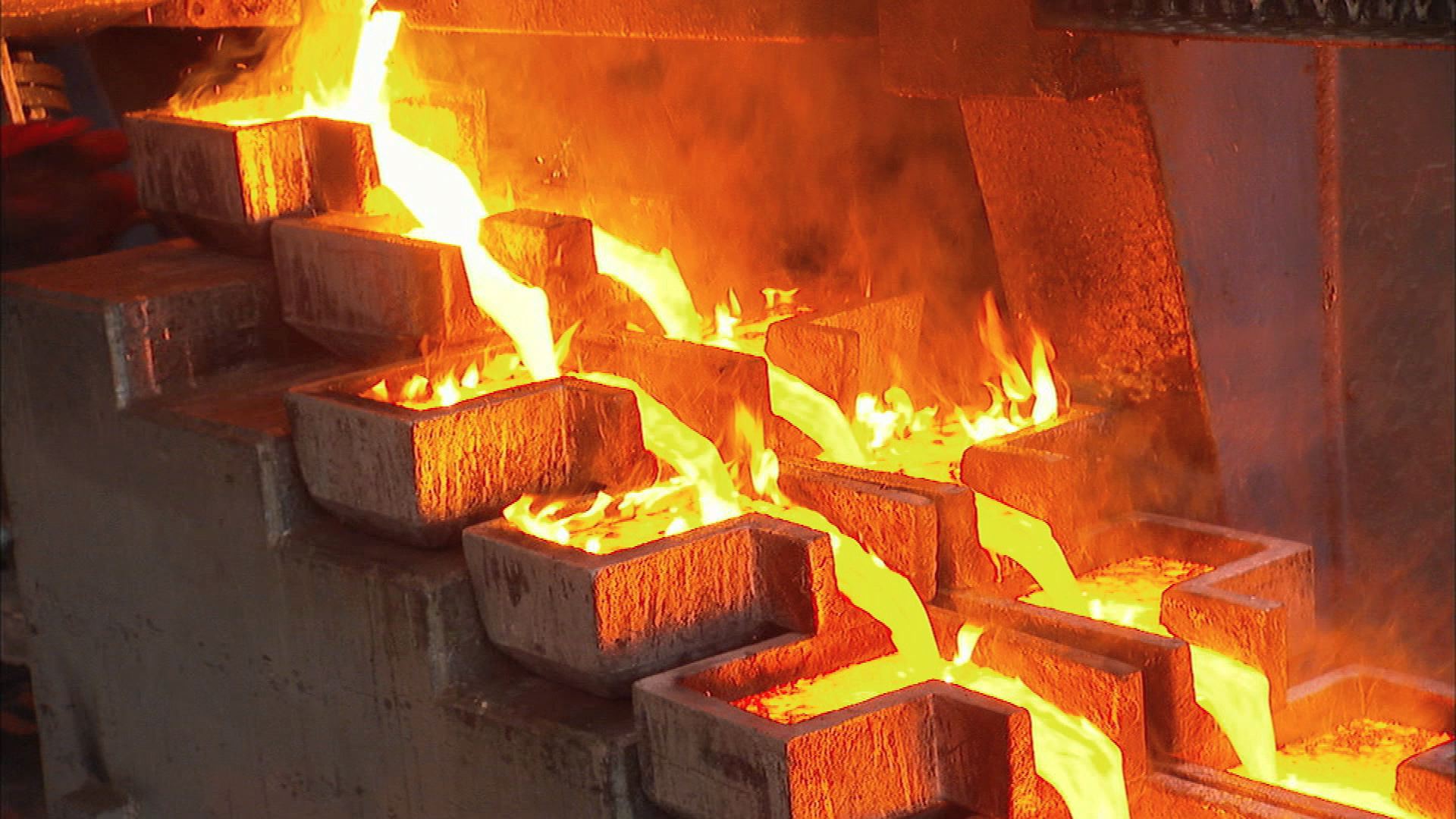
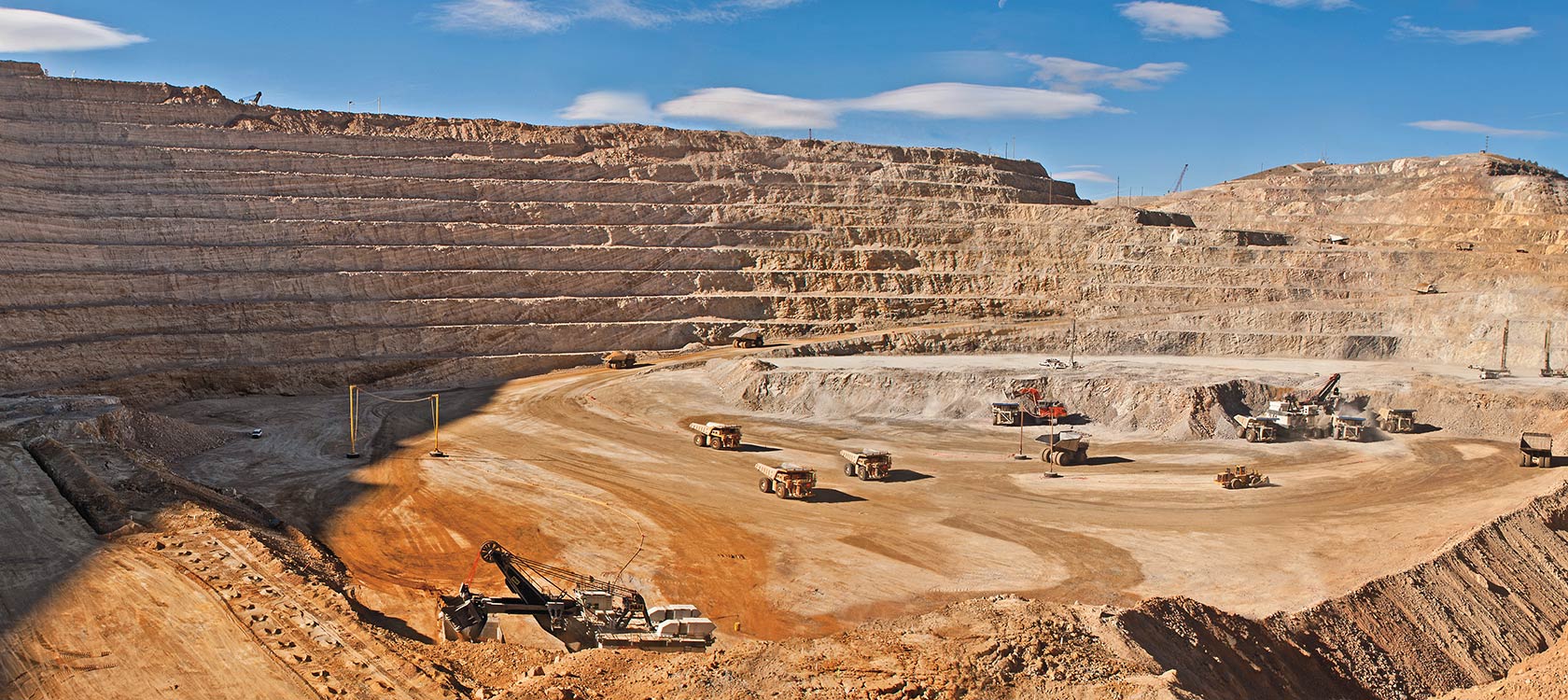
What really gives gold it’s value is the cost of exploration and production. Being very rare it takes a lot of effort to find gold. Once it’s found it is expensive to produce as well. For example Barrick’s Cortez mine in Nevada has an average grade of 2.11 grams per ton. That means that for every ton of ore processed they average 2.11 grams of gold. Barrick’s published production cost at the Cortez mine is about $900/oz. It really is remarkable that they can move and process the 15 tons of rock required to obtain an ounce of gold for $900.
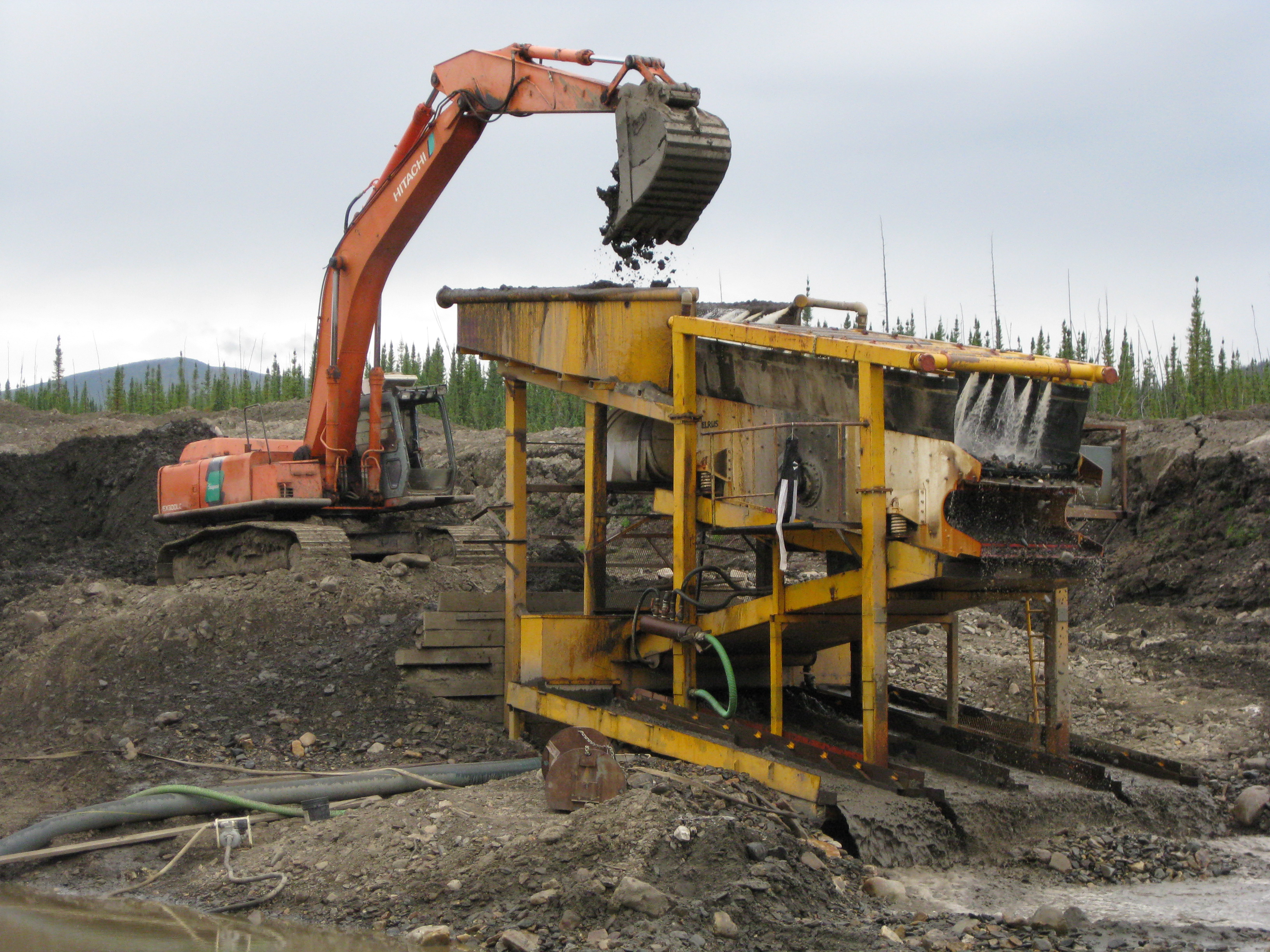
The cost of producing an ounce of gold varies for each mine. In a placer operation it is a constant cat and mouse game to keep costs low enough to make production economical. When gold commodity prices fall below production costs mines shut down and less and less gold is produced. The production cost, driven by scarcity is the single most important factor that drives the price of gold.
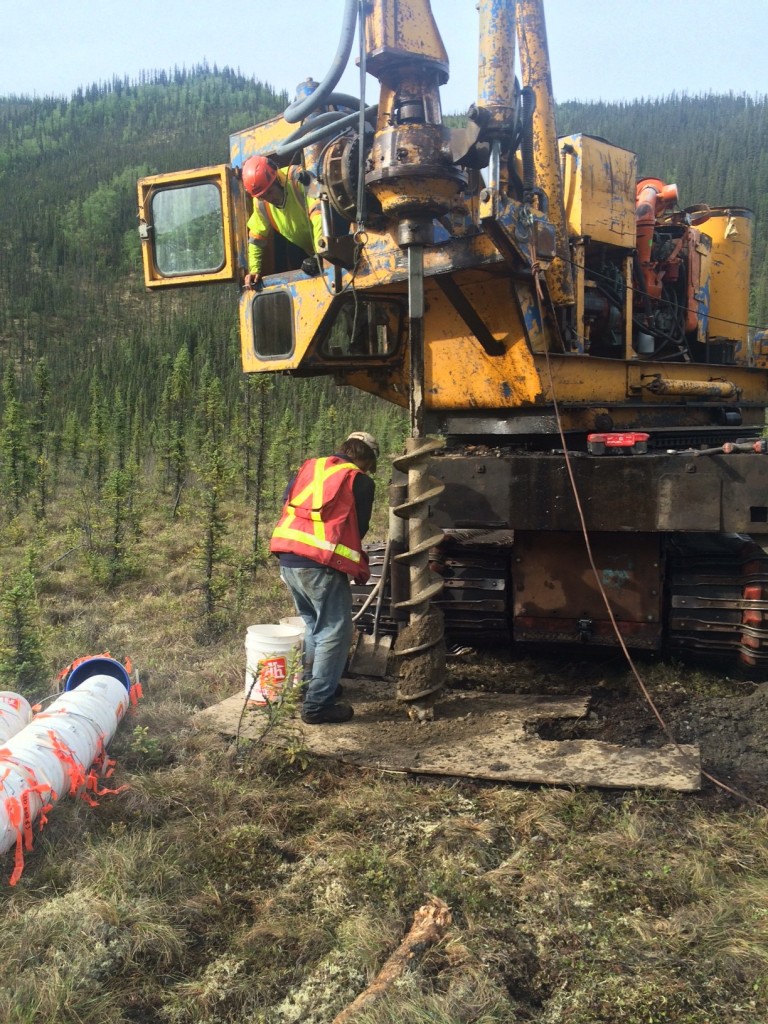
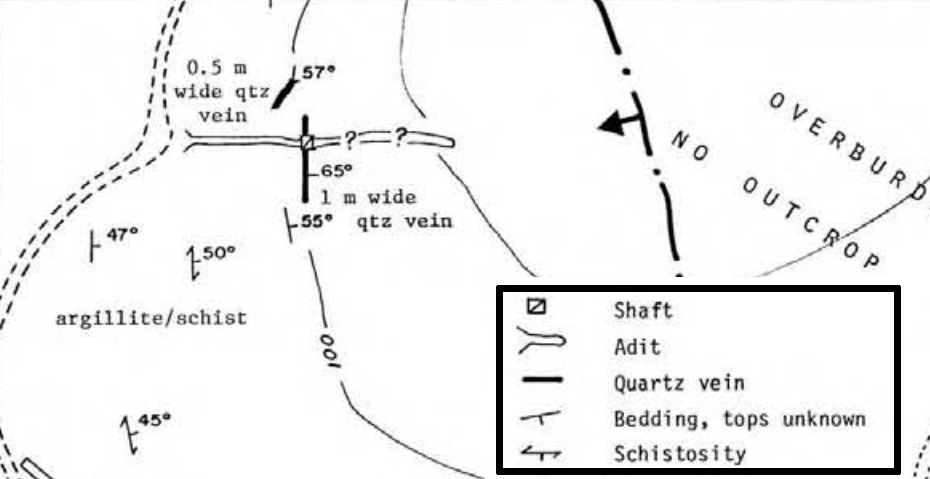
Gold exploration is also very expensive. In the times of the North American gold rush placer and hard rock gold was discovered all over the Western part of the continent. From the 1840s to 1900 new gold districts were popping up every year as discoveries were made. Trending almost in sequence Northward from California to the Yukon as explorers made their way through the wilderness. In more modern times most of the easily reachable areas have have been at least partially explored. Exploration today mostly takes place in more and more remote areas, such as the Canadian Arctic or other places with a small human footprint.
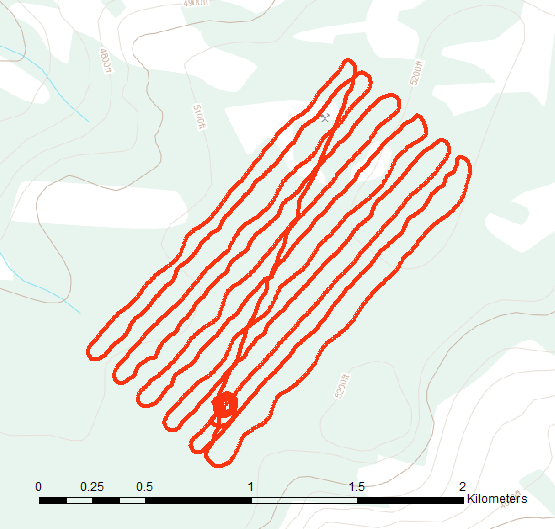
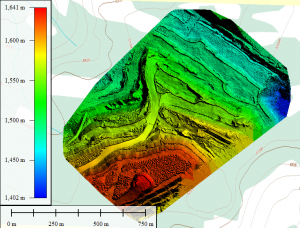
To properly explore a claim in these areas requires a camp. helicopters and all kinds of equipment. A typical small exploration program in the Northwest Territories can cost well over $1,000,000 per season with slim chances of success. While advancements in exploration technology such as geophysics and aerial imagery can provide information that wasn’t available to previous explorers there is no silver bullet.
The costs of thousands of exploration ventures that didn’t amount to a mine are factored into the price of gold as well. For the estimated 100,000 explorers that took part in the Yukon gold rush only a select few managed to recoup their costs. Some made made great discoveries but many more spent their life savings on an adventure but returned with no gold.
Gold’s value is based on it’s unique properties, people’s desire for the very special metal and the work required to find and produce it. The value has nothing to do with the the dollar value attached to it. For every ounce of gold produced tons of rock had to be excavated, the deposit had to be discovered and mapped, and the ore milled and smelted to extract the gold. As you gaze upon your gold ring and admire it’s beauty think about the story that it could tell you.